
Structure of a CanvasMap Web Page
If you look at the HTML file in the previous tutorial, you'll see there are a number of sections to the web page. The sections are identified with HTML comments in the previous tutorial and outlined below.
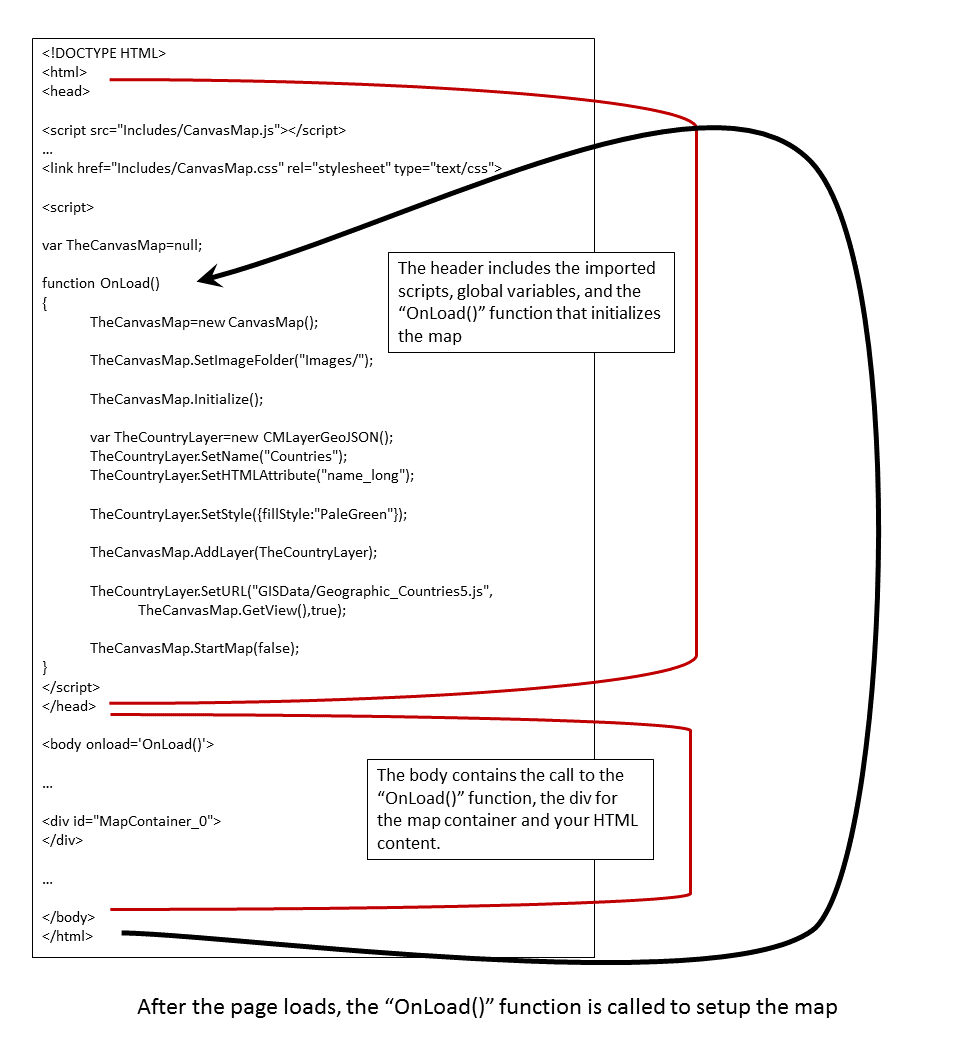
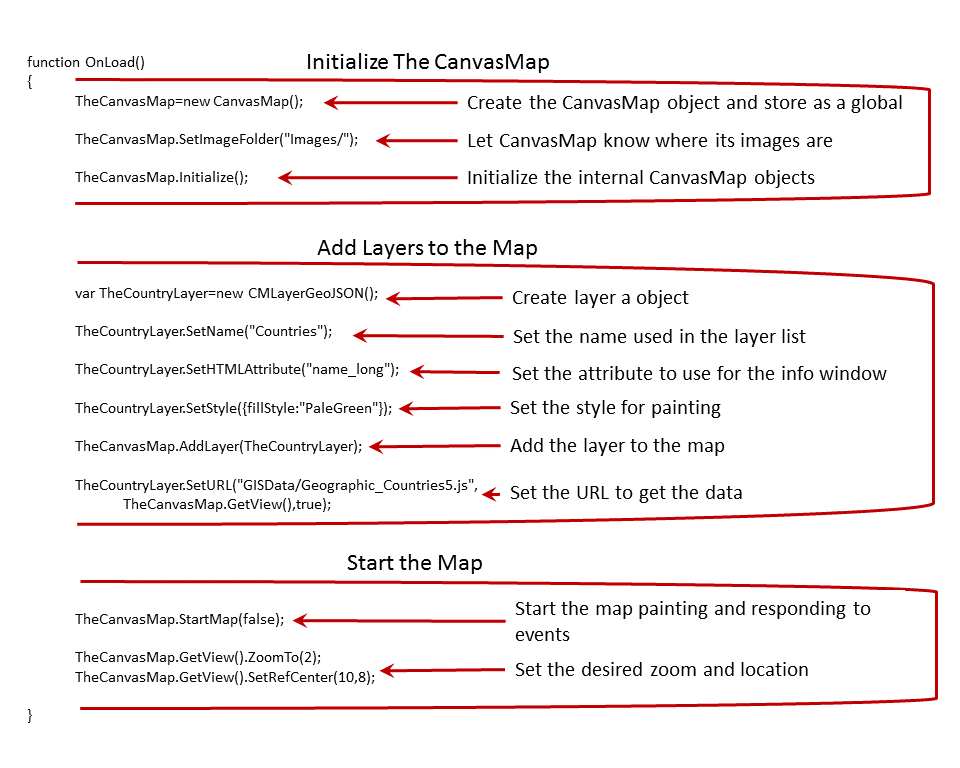
Most of the action is in the "OnLoad()" function. Below is a diagram showing what is happening in each section:
The links below will take you to code samples for two maps containing simple vector data. One sample works if you have a web server available and the other one works from a file system. One one of the files and then open the debugger in your browser ("three dots" -> More Tools -> Developer Tools, in Chrome).
- Simple Map to Get Data From a URL - uses a URL to get the data and requires a web server
- Simple Map to Set Data from a Local File (Geographic_World_SetData.html) - only uses local data, does not require a web server (you'll need to run this map by double-clicking on it in the file explorer).
There are a number of JavaScript files included and you only need to include those that are needed for your specific map. CanvasMap also uses jQuery so you'll need to load a version of it. We include one that is compatible with the current version of CanvasMap.
The only function we need for the default map below is an "initialization" or "init()" function to setup the map with the desired layers. We also need to have a global variable to hold on to the CanvasMap object. This is the main object that we will interact with in future tutorials to customize the map.
The body of the HTML just has the one tag we need for the "MapContainer_0" element. This is the element that the map will be placed into when "Initialize()" is called.
Initializing the map
Take a look at the "OnLoad()" function and you'll see code to initialize the map, add layers, and start the map. Note that you cannot add layers to a map until after the map is initialized.
The code below will:
- Create the CanvasMap object and save it to the global variable
- Set the location of the images folder. This tells CanvasMap where to find the images. The current setting should work as long as you have your maps stored in the "CanvasMap" folder. If you move them, you'll need to update the image folder.
- Initialize the CanvasMap. The "Initialization()" function sets up the internal state of the CanvasMap so we can add layers to it.
TheCanvasMap=new CanvasMap(); // creates the map object
TheCanvasMap.SetImageFolder("Images/"); // lets CanvasMap know where the images are
TheCanvasMap.Initialize(); // sets up the view, scene, and event handlers for the map
The code below adds a layer to the map. "CMLayerGeoJSON" displays polygon and linestring (i.e. polyline) data in the map. There are other layer types we'll learn about in future tutorials. This code takes the following steps:
- Create the layer
- Give the layer a name which will appear in the layer list
- Set the URL for where the data is located. Note that we also send the layer the "CMView" that is within the CanvasMap (more on this later) and a flag "true" indicating we want CanvasMap to "ZoomTo" this layer after it is loaded. Note that if you are running without a server and used the "Set Data" page, you'll have a "SetData()" function instead of the "SetURL()" function.
- Set the style of the layer to be filled with "PaleGreen"
- Add the layer to the CanvasMap
var TheCountryLayer=new CMLayerGeoJSON();
TheCountryLayer.SetName("Countries");
TheCountryLayer.SetURL("GISData/GoogleMercator_Countries_100m.js",TheCanvasMap.GetView(),true);
TheCountryLayer.SetStyle({fillStyle:"PaleGreen"}); // fill the data with pale green color
TheCanvasMap.AddLayer(TheCountryLayer);
The final step is just to call "StartMap". We have specified a flag of "false" to keep CanvasMap from resizing the map to fit the browser window as the default is to create a resizable map (more on this later).
TheCanvasMap.StartMap(false); // don't resize